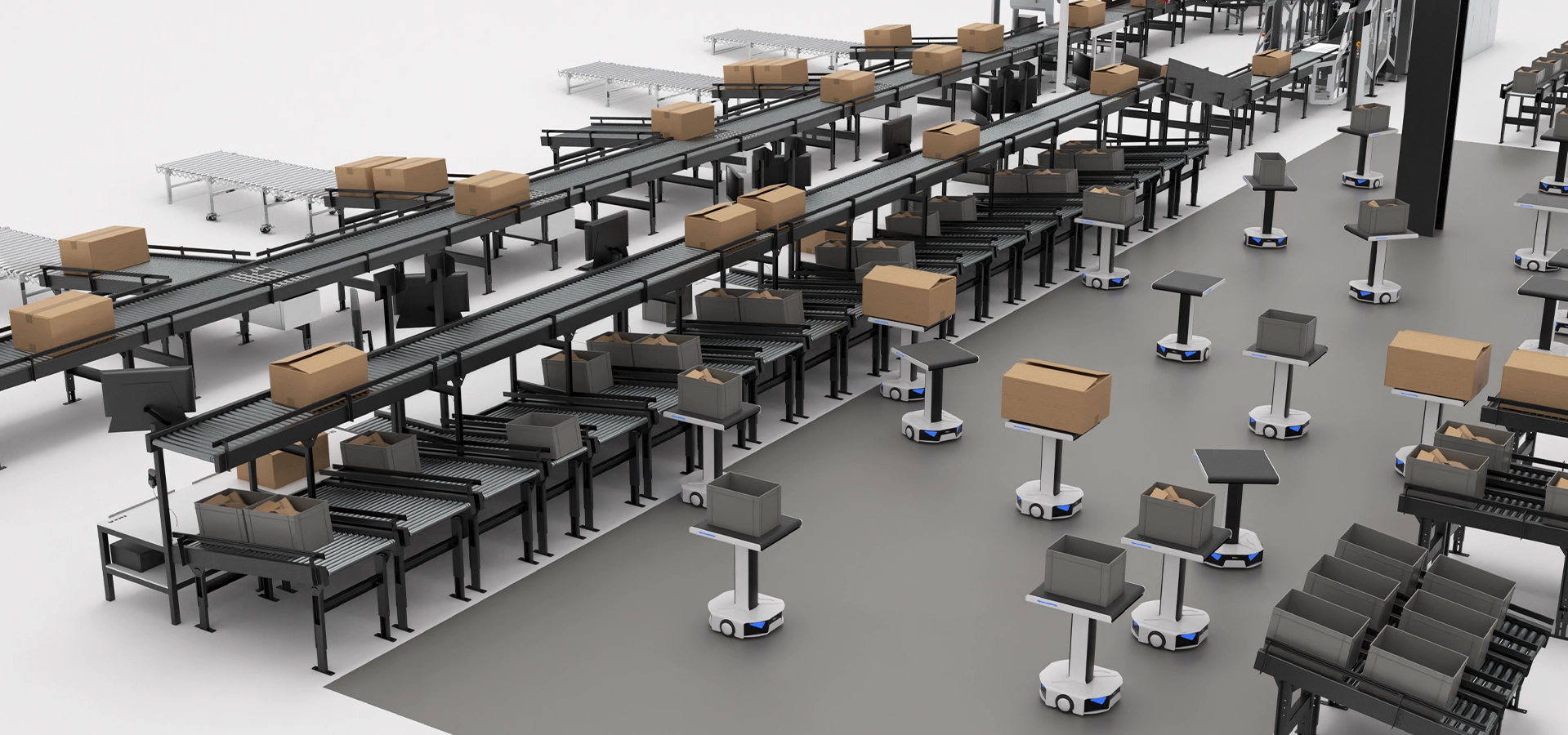

Intralogistics is one of the key links for many companies. The quest to improve productivity, efficiency and speed within warehouses has led to the incorporation of advanced technologies. One of these is automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
According to a study by consultancy Grand View Research, the global AGV market is expected to continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.2% through 2030.
In this post we will see what these automated vehicles are all about and when and how it is the best way to incorporate them in your logistics center.
What are AGVs?
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are robots used to transport goods between different areas of the warehouse or between connected installations, without the need for human intervention. They automate the repetitive movement of products, streamlining flows within logistics centers and ensuring a safer environment for operators.
How do AGVs work?
The AGVs are equipped with a sensor-guided system as well as proprietary software that can be integrated into a WMS (warehouse management software) or WCS (warehouse control system).
The control software of the automated guided vehicles is responsible for managing and programming the routes. The robots receive instructions on the movements to be made and report on their work in real time. As a result, they can move around the logistics center without the need for a driver.
Although the route must be predetermined and the speed of movement controlled, AGVs also have technology that ensures the safety of operators and the products handled, such as scanners, intelligent sensors or safety bumpers. This technology allows them to detect people and objects, thus avoiding accidents in the workplace.
Types of AGVs
There are several types of AGV robots, among which are:
- Forklift AGVs: commonly used in large distribution centers, these robots are designed to move one or more pallets and perform functions similar to forklifts, but automatically.
- Unit load AGVs: designed to transport one unit per trip, such as boxes, coils, pallets, among others.
- Material handling AGVs are used to move and handle goods, and can perform loading and unloading of goods.
- Tow tractors: mobilize other non-motorized systems, facilitating loading and unloading on a trailer or freight train.
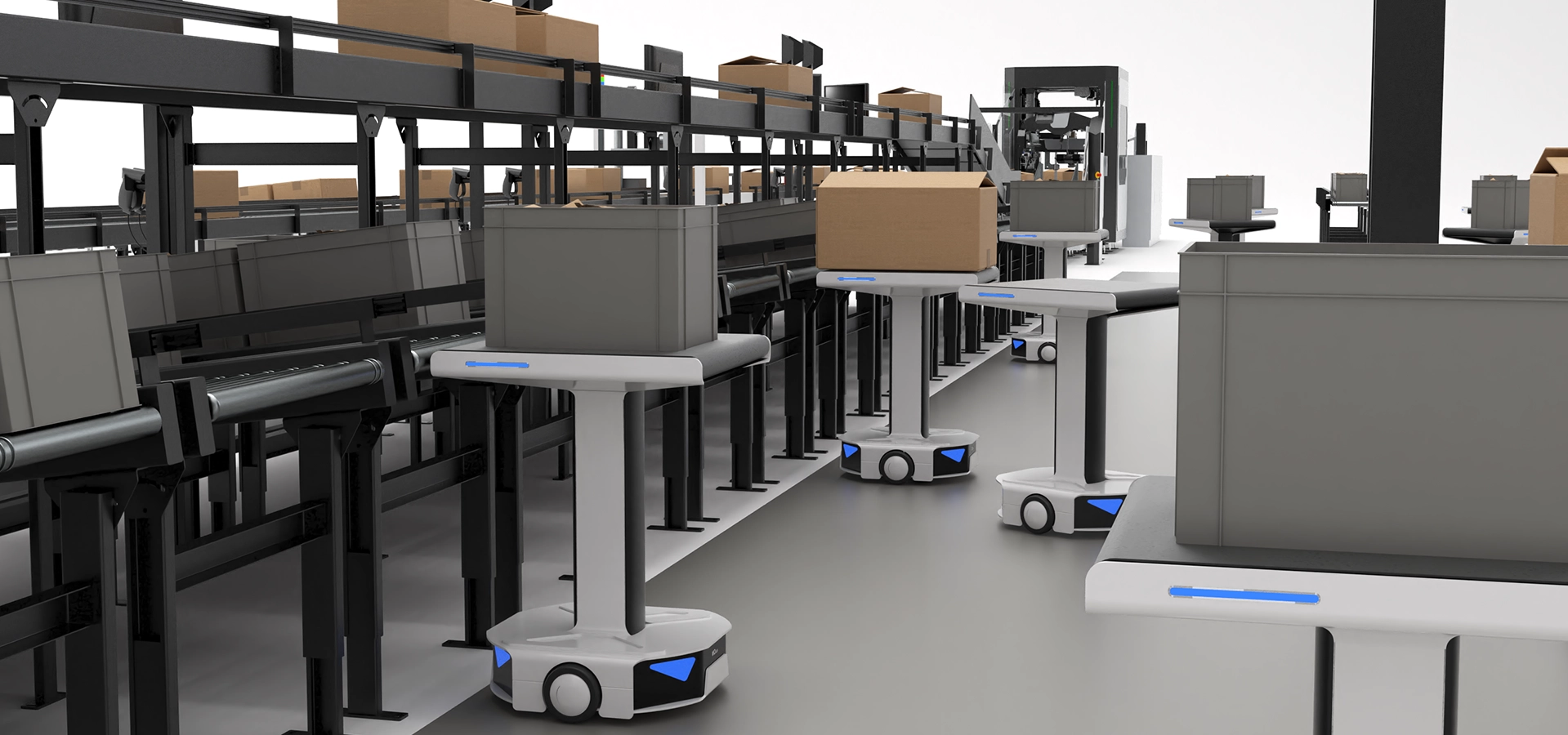

AGVs can also be classified according to their guidance system:
- Filoguided: robots use a conductive wire installed under the floor to move. It is used for repetitive and uniform load flows.
- Laser guided: they are equipped with a laser that allows them to determine their position in real time within the logistics center.
- Geo-guided: the robots create a map of the warehouse and move freely thanks to built-in sensors.
- Optoguided: a catadioptric mirror strip sets the path that the AGV must follow. The robot's photocells allow it to detect and follow the path.
- Artificial intelligence: thanks to the use of artificial intelligence 360º cameras, the robot can determine the best route to follow.
Advantages of automated guided vehicles AGVs
Incorporating this type of technology into a warehouse has several advantages that impact the company's profitability.
- Avoid human error
- Reduces occupational accidents
- Streamlines movements within the logistics center
- Reduces operating time
- Contributes to homogeneous supply flow
- Allows for continuous, full-time work cycles
- Reduces operating costs
- Enables workers to perform higher value-added tasks
Disadvantages of automated guided vehicles AGVs
While automated guided vehicles have many advantages, it is important to note that they may not be ideal for all types of jobs. For example, with the exception of AI-guided AGVs, they can be an inflexible solution, as most move through rigid systems that require uniform product flows. In addition, AGVs are used for unit load, so they are likely to require other complementary systems to handle high order volumes.
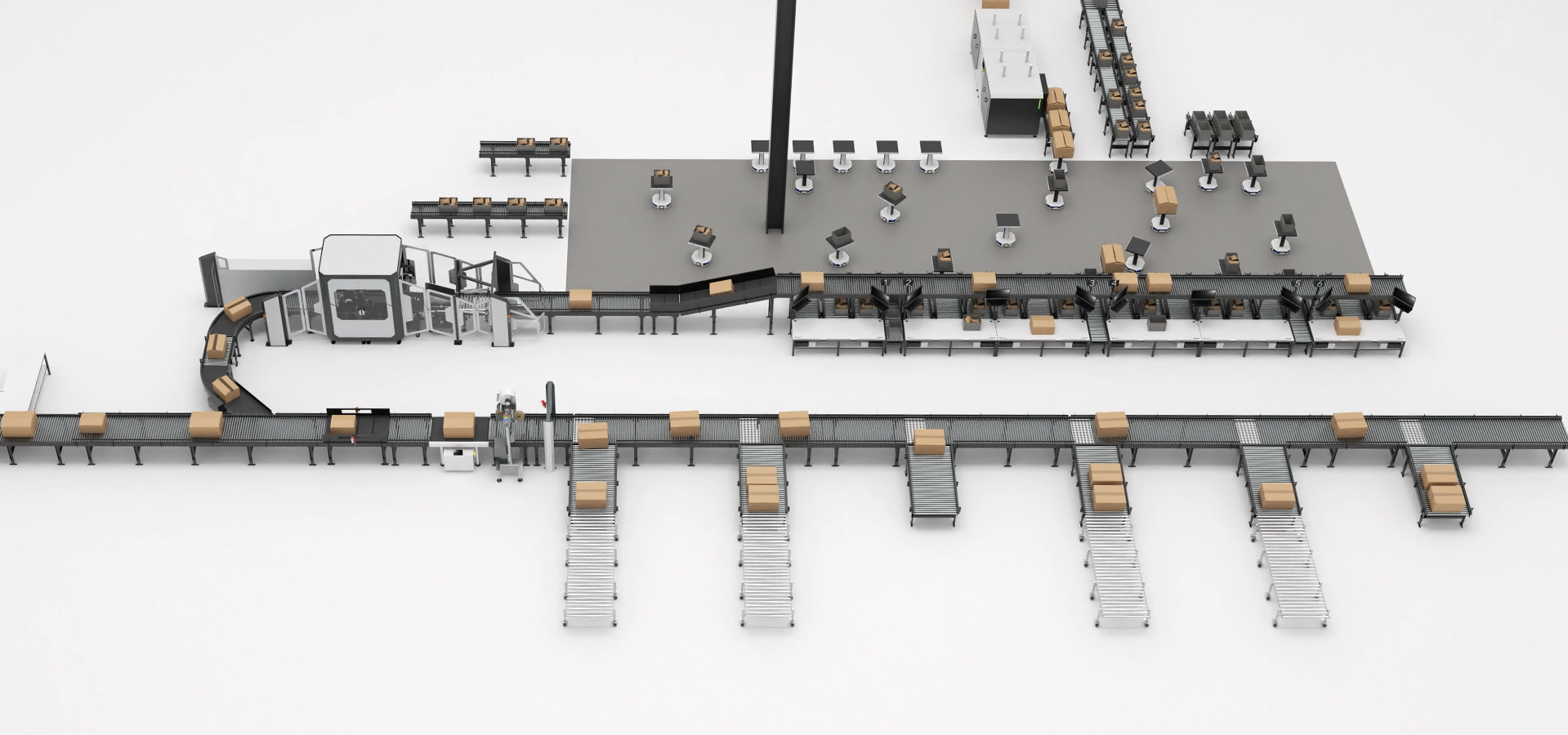
When is it recommended to incorporate automated guided vehicles AGVs?
AGVs are recommended for industrial contexts, where efficient and safe transport of loads is required. This type of technology is very common in logistics centers that work under the just-in-time or lean manufacturing method. AGVs can supply raw materials to production lines, reducing process times and costs, and ensuring employee safety.
However, it is important to note that AGVs are not usually the most suitable solution on their own. No matter how small a project is, it is always advisable to incorporate other automatic solutions, such as conveyor belts. In this sense, AGVs are ideal when used as complements, and can be added for the beginning, during or end of an intralogistics process, as well as for transporting goods from one area to another. An example of this would be using a belt conveyor to move materials, and having a robot to receive them.
So, the best solution? Complementing automated warehousing and transport systems with AGVs.
Integration of an automated warehouse with AGVs
As mentioned above, incorporating AGVs to an automated warehouse has many advantages, as well as including automations when you want to work with these robots. At Rielec we manufacture customized intralogistics solutions so that you can improve the efficiency of your warehouse. We take care of their manufacture and assembly, but our after-sales service also allows us to accompany you after the completion of the work. We also work with partner companies that offer AGVs in order to design the perfect project for each customer. If you are interested in automating your warehouse, you can contact us here.